This wearable device is designed to enable the quantitative measurement of an infant’s motor development through their spontaneous kicking patterns, potentially providing earlier detection of motor dysfunctions and delays that are common in conditions such as cerebral palsy. The technology package includes a fabric circuit attached to infant pants and equipped with six sensors as well as a single voltage source and voltage regulator that wraps around the infant’s leg. It utilizes gyroscopes and accelerometers at 100 Hz and then transfers kicking pattern data to a mobile application wirelessly. The technology displays the data graphically for a clinician’s easy analysis.
By placing sensors on three areas of the leg—thigh, shin, and foot—Georgia Tech’s innovative method for gathering information about the movements of each limb segment relative to the others and overall gross leg movement could provide a detailed assessment of motor development. This infant suit may allow for the long-term, in-home collection of quantitative kinematic kicking data outside of a clinical setting. In addition, clinicians could potentially analyze this data offline and, in turn, provide earlier detection of motor dysfunctions like cerebral palsy.
- Advanced: May allow for earlier detection of motor dysfunctions in order to begin therapeutic interventions as soon as possible
- Robust: Collects data from three limb segments on the leg for a multifaceted assessment
- Long-lasting: Uses one power source with regulated voltage in order to prolong the use of the device
- Adjustable: Enables the suit to grow with the infant
- Cerebral palsy
- Dystonia
- Ataxia
- Myoclonus
- Other neurodevelopmental motor disorders
Spontaneous kicking is one of the earliest displays of motor skills and is an important precursor to later voluntary motor control. Typically, evaluations for motor abnormalities are done qualitatively through observation of motor milestones in a clinical setting. This approach, however, does not always allow for diagnosis early enough to optimize an intervention’s effectiveness and is sometimes unreliable because of differences in clinician opinion. This Georgia Tech infant suit device, method, and algorithms may provide a potential solution.

The fully fabricated infant suit with the device on one leg
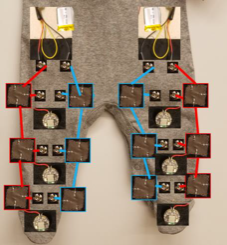
Layout of the infant suit components
