The SlothBot is a solar-powered, wire-traversing robot designed for long-term environmental monitoring applications. Its unique ability to easily switch between branching wires allows it to survey a wide area. It also provides a fail-safe as it keeps the robot attached to a wire at all times. SlothBot takes advantage of its simple and compact system design to reduce maintenance as well as the risk of failure. The robot uses solar power to recharge its battery. It also leverages slowness as a design principle—in stark contrast to conventional robotic strategies—in order to be as energy-conserving as possible. Slowness and long-term sustainability make SlothBot perfect to study environmental changes over extended periods of time.
A key feature of the SlothBot is its unique and modular mechanical setup, composed of standalone bodies connected by actuated hinges. Each body contains a motor, a wheel and four spur gears. Two of the spur gears are c-shaped, allowing the body to either remain locked onto the wire or turn depending on their position. Compared to existing robotic wire-switching systems, these features make Georgia Tech’s SlothBot significantly more energy efficient and lower risk.
- Wide-ranging: Can switch between two different wire branches and can therefore traverse a whole mesh of wires
- Sustainable: Utilizes solar energy and runs with a low power consumption, making the robot highly energy efficient
- Low risk: Employs a fail-safe design that protects the robot from damage in the event of a mechanical failure
- Environmental monitoring
- Conservation research
- Precision agriculture
- Autonomous sensing/monitoring equipment
Wire-traversing robots are often useful in environmental monitoring and agricultural applications as well as for monitoring and maintenance in hazardous settings, such as on a power line. However, many conventional designs for these applications require multiple battery changes due to their high power consumption and are not always capable of wire-switching, limiting their coverage area.
The Georgia Tech SlothBot was designed with total self-sustainability in mind. It remains attached to the wire at all times and autonomously seeks out solar energy when its power is low. For these reasons, the SlothBot is the ideal robot for tasks over an extended period of time, supporting crucial information-gathering efforts for climate change research and conservation.
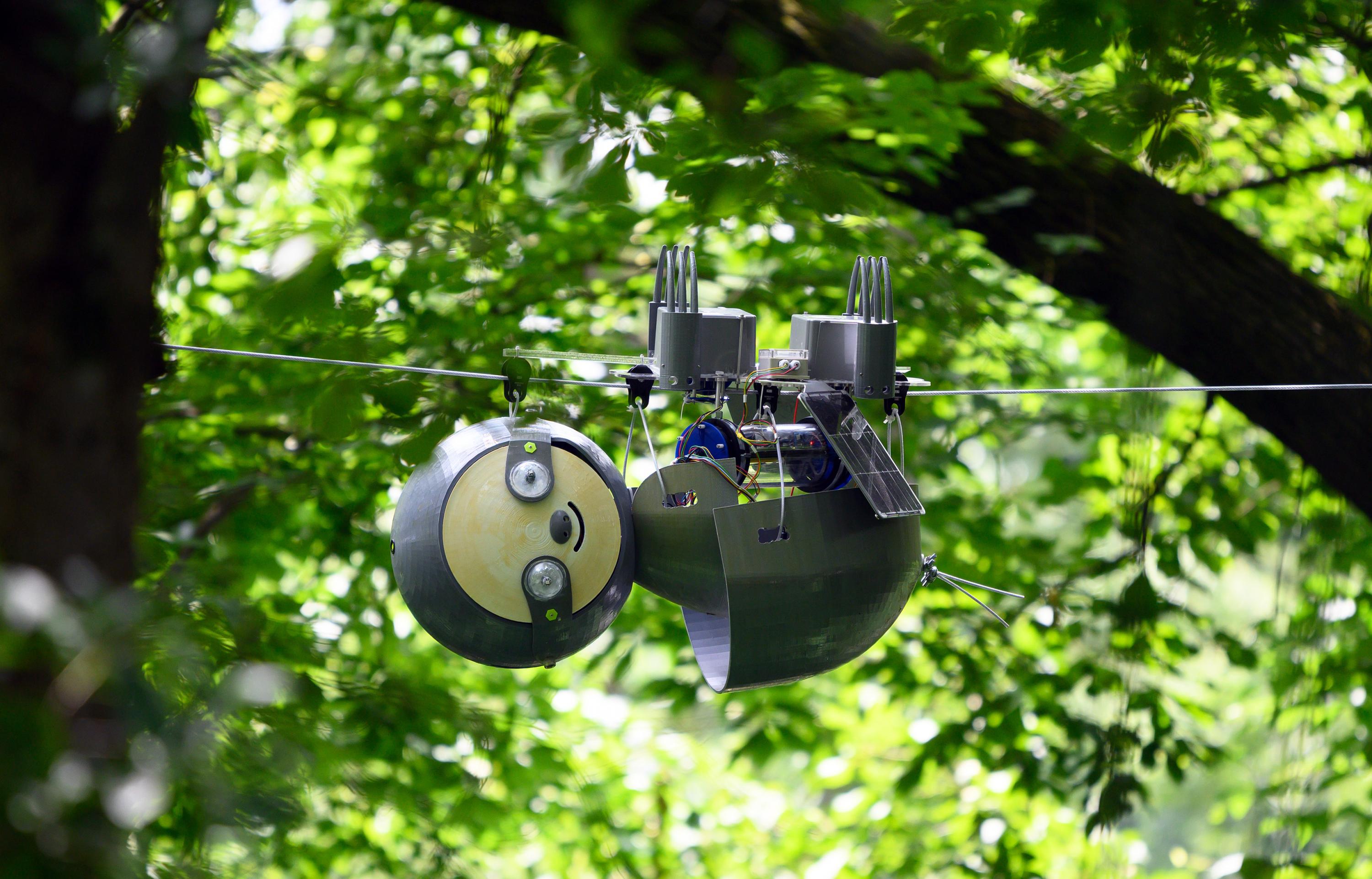

SlothBot in the canopy of the Atlanta Botanical Garden
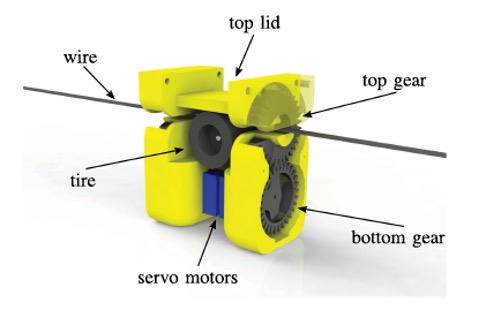
A diagram of one of two bodies that make up SlothBot and its labeled components
