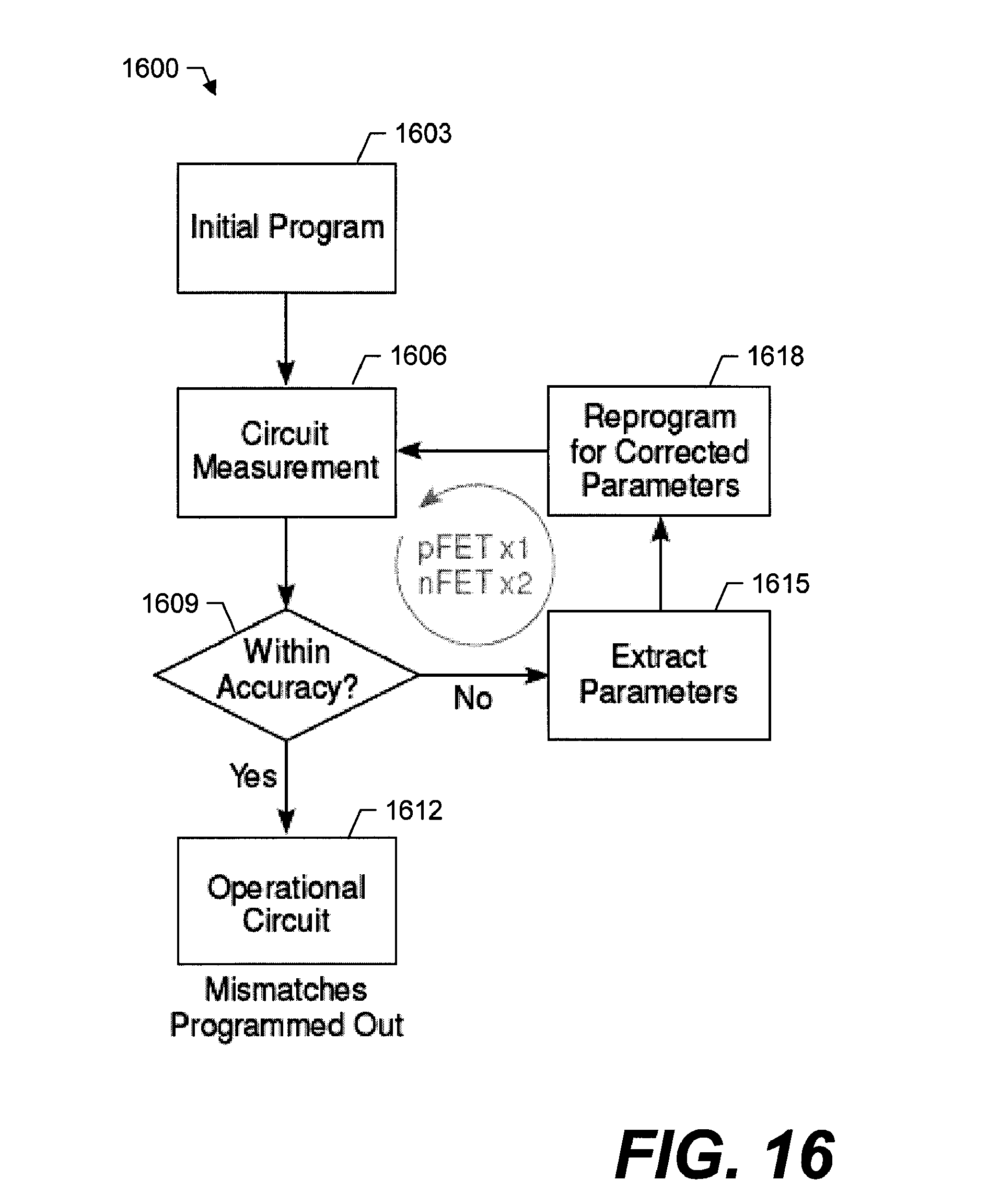
Georgia Tech inventors have created a floating-gate transistor array and method for programming it. The floating-gate transistor array includes a plurality of transistors having a source, drain, and floating-gate, whereby the plurality of transistors is arranged into multiple rows and columns. Each row of transistors includes a row programming switch having an output connected to each floating-gate within the row, while each column of transistors includes a column programming switch having an output connected to each drain within the column.
- Precise
- Smaller switch count
- Fewer parasitic
- More efficient
- Programming multiple current sources
- Flash memory
- Storage devices
As the industry pushes toward shorter design cycles for analog integrated circuits, the need for an efficient and effective field-programmable analog array (FPAA) becomes paramount. Indeed, the role of analog integrated circuits in modern electronic systems remains important, even with the advent of digital circuits. Analog systems, for example, are often used to interface with digital electronics in applications such as biomedical measurements, industrial process control, and analog signal processing. More importantly, analog solutions may become increasingly competitive with digital circuits for applications requiring dense, low-power, and high-speed signal processing.